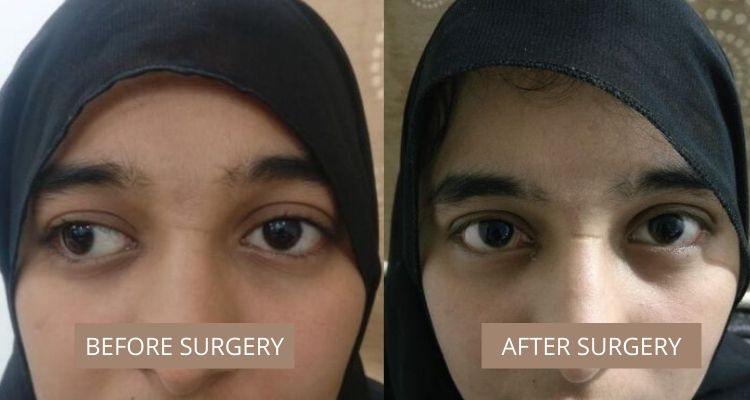
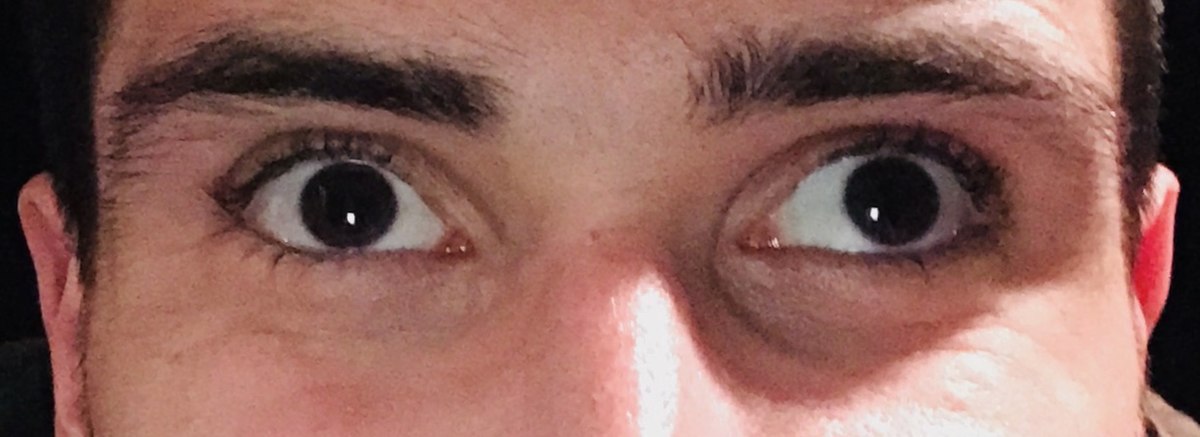
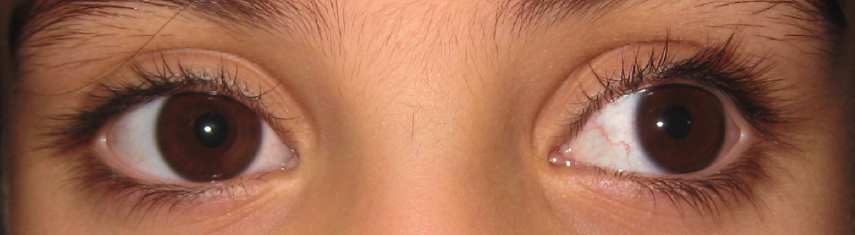
Exotropia — a common type of strabismus — is the outward deviation of an eye (away from the nose) The deviation or eye turn may occur while fixating (looking at) distance objects, near objects or both When the eye turns outward at all distances andWith intermittent exotropia, one or both eyes look in an outward direction only when the person is ill or tired, or when they are looking into the distance (intermittent distance exotropia) The rest of the time their eyes are aligned straight (as normal) Exotropia is a type of strabismus characterised by outward deviation of an eye One of both eyes may be focused away from the eye under normal conditions This may be noticed while looking at a distant object, a nearby object or while both There are 2 types of exotropia

Vision Therapy Success Story Strabismus Exotropia Eye Turn Outward Vision Therapy Philippines
Exotropia of both eyes
Exotropia of both eyes- Strabismus is when there's a deviation of the eyes that you cannot control Both exophoria and exotropia are conditions that cause the eyes to drift outward Both conditions may also be referredWhat is intermittent exotropia?




Exotropia In Cromwell Ct 4d Vision Gym
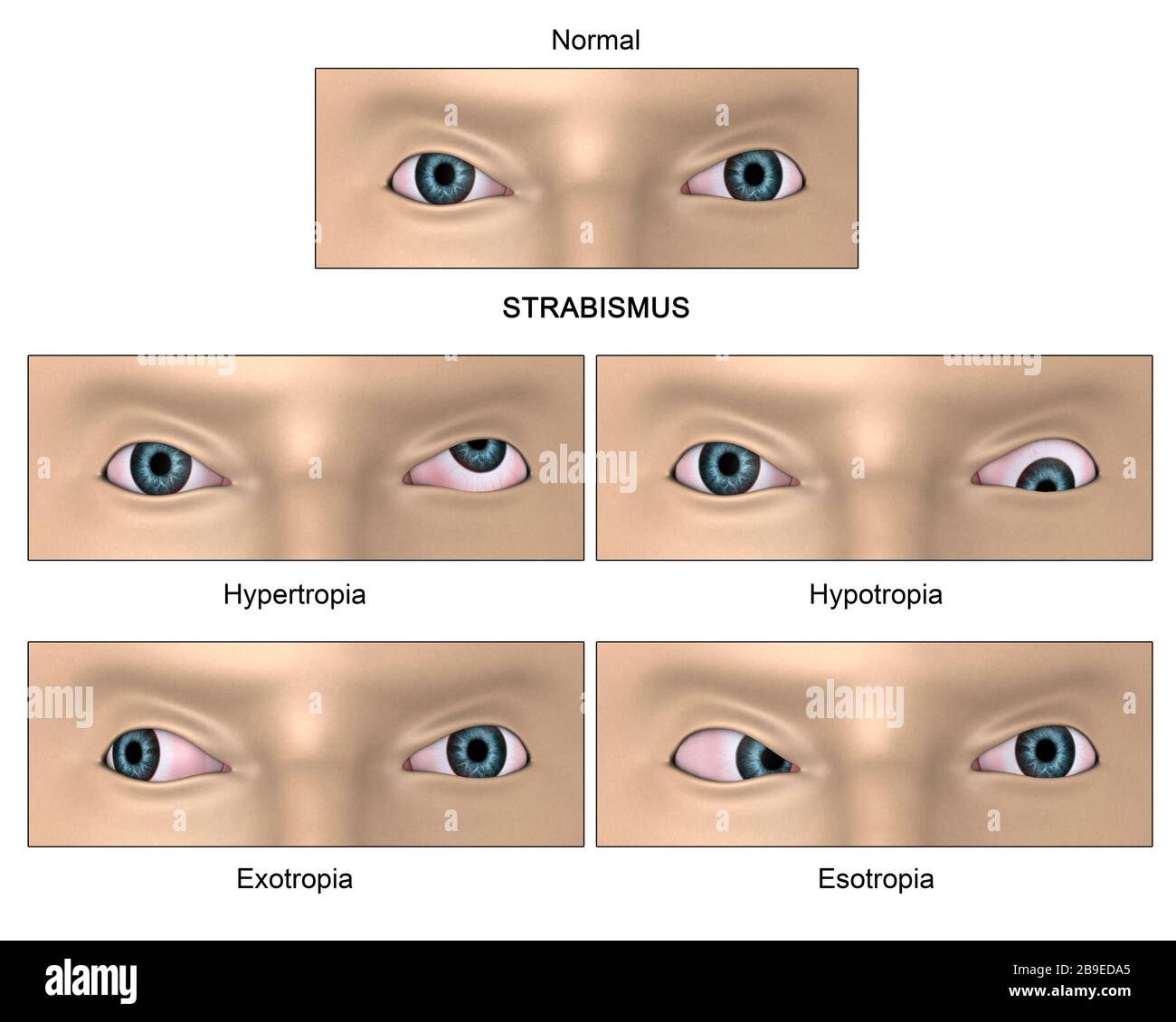
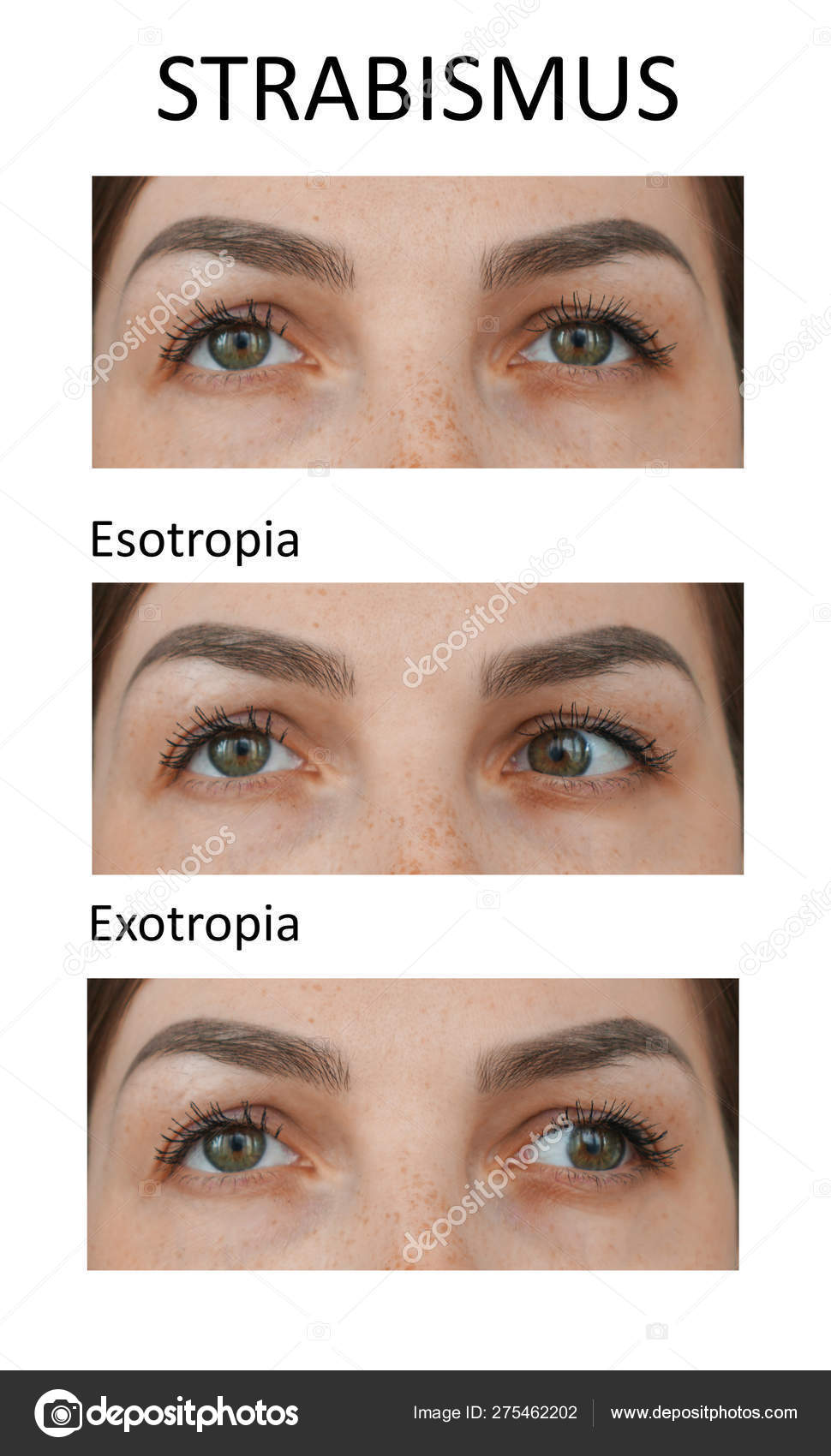
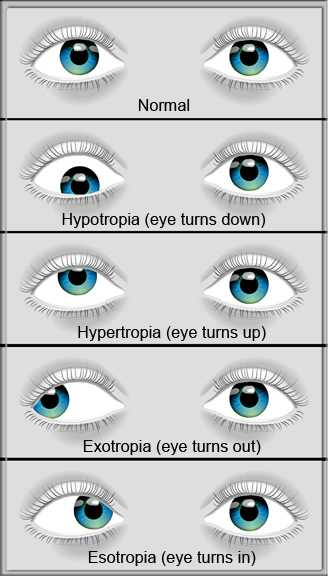
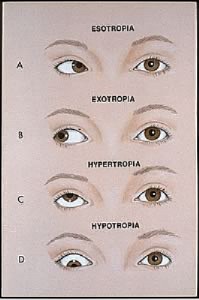
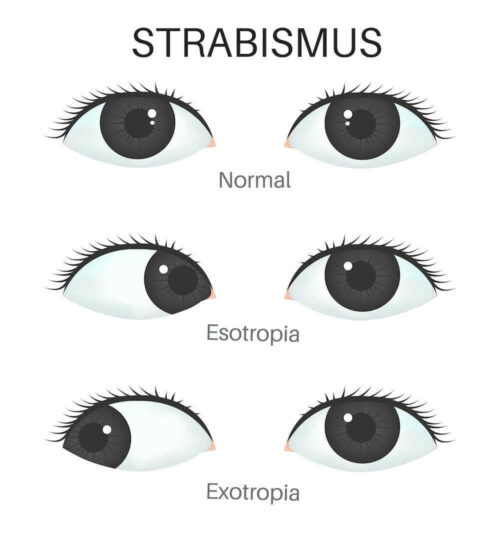
Tap card to see definition 👆 Strabismus characterized by an inward deviation of one or both eyes is known as Click again to see term 👆 Tap again to see term 👆 Xerophthalmia Click card to see definition 👆 Tap card to see definition 👆 The drying of the surfaces of the eye, including the conjunctiva, is calledEsotropia and exotropia are types of strabismus, which is a condition in which the eyes are not properly aligned Esotropia means that one eye is deviated inward and is often called crossed eyes Exotropia is when one or both eyes look outward, often called walleyed Although newborns' eyes may wander or cross sometimes, the eyes usually straighten by 2 to 3 months of ageWhat is Esotropia Esotropia, a form of Strabismus, is the inward deviation (turn) of an eye and occurs in 12% of children by 7 years of age and occurs equally in males and femalesIn esotropia, one or both eyes turn in while in exotropia one or both eyes turn out Pseudoesotropia refers to the appearance of crossed eyes in a child whose eyes are actually perfectly aligned in relation to
Exotropia in Adults This material will help you understand exotropia and how to manage it What is exotropia?Pretty much everyone, including myself, looks like they got stabbed in the eye after the operation Lucky you Looks great 2 Reply Share Report SaveIntermittent exotropia can happen at any age Treatment may involve glasses, patching, eye exercises and/or surgery on the muscles of one or both eyes Another type of strabismus is called infantile esotropia This condition is marked by a large amount of inward turning of both eyes in infants that typically starts before six months of age
Exotropia belongs to a condition in which one or both eyes turn out from the nose It is the opposite of crossed eyes While it can affect anyone at any age, it is commonly diagnosed at a young age and accounts for up to 25 percent of all eye misalignments in young children Exotropia is a eye turn where one eye points outwards, this may be noticed while the child is looking at distance objects, near objects or both There are two types of exotropia Constant;In rare instances, both eyes are facing inwards Often people confuse esotropia with a lazy eye, but actually these conditions are quite different Esotropia is a type of strabismus (squint), where the eyes are misaligned, which causes the eyes to look inwards and can prevent the eye perceiving images in depth
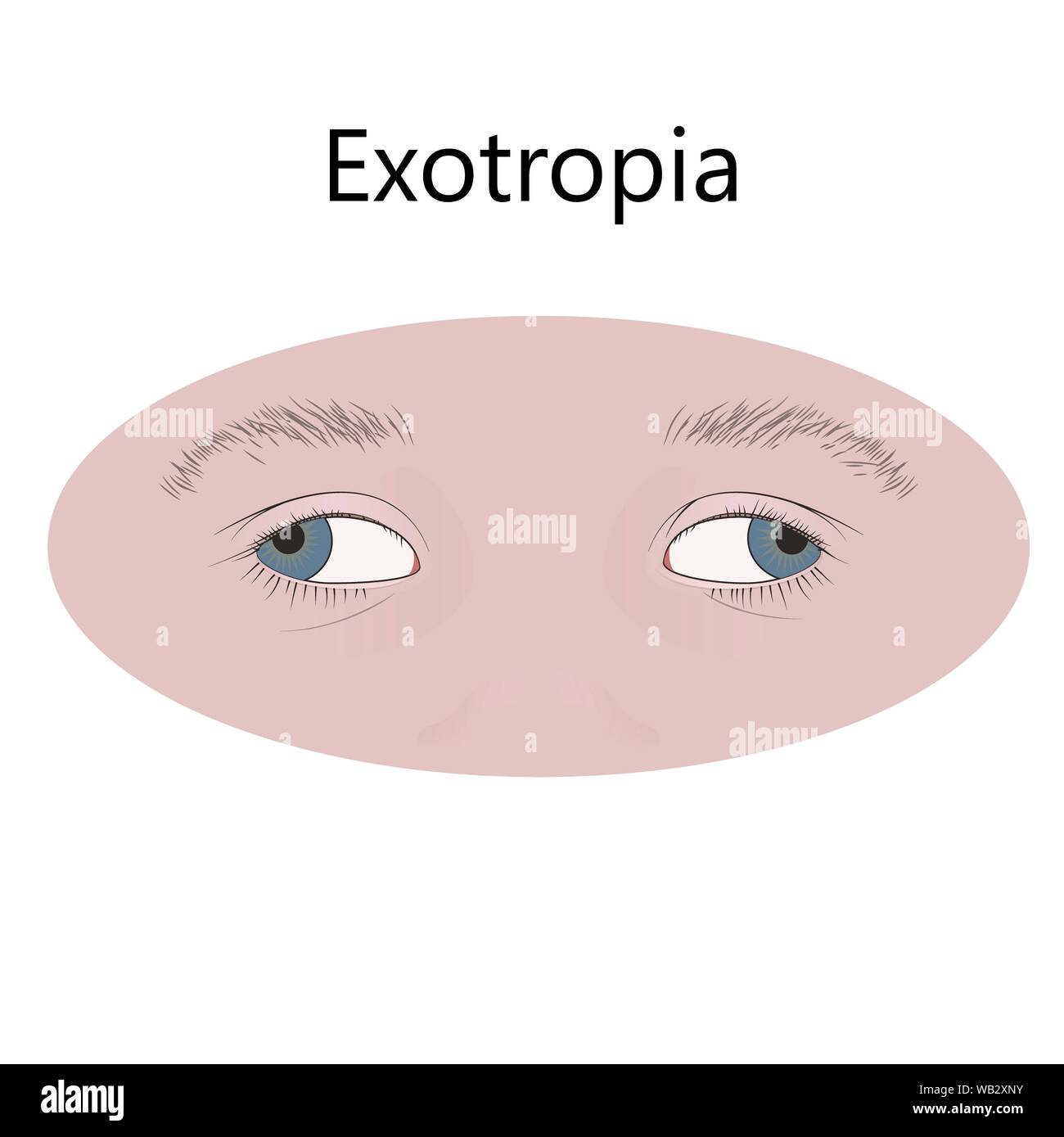



Exotropia High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



Esotropia Wikipedia
Exotropia is a type of strabismus (eye misalignment), where one eye turns, or deviates, outward (away from the nose) The deviation may be constant or intermittent, and the deviating eye may always be one eye or may alternate between the two eyes The deviation or eye turn may occur while fixating (looking at) distant objects, near objects, or both Exotropia H501 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail The 21 edition of ICD10CM H501 became effective on This is the American ICD10CM version of H501 other international versions of ICD10 H501 may differOptions for 4 year old with intermittent exotropia My daughter has intermittent exotropia, both eyes No issues with vision Opthamologist visits for 18 months Now booked for surgery Both eyes He suggested patches wouldn't work for her Concerned about the failure rate, overcorrection and future multiple surgeries




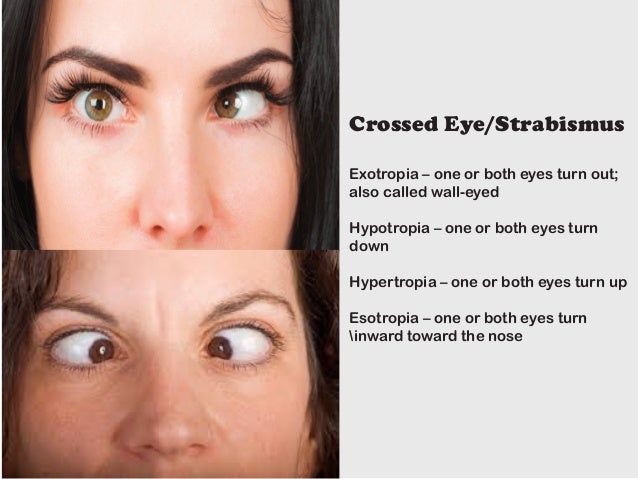
Ophthalmologists Strabismus Or Crossedeyes Is A Condition Where Both Eyes Do Not Look At Same Place Time Classified By Eye Turn Inward Turning Esotropia Outward Turning Exotropia Upward Turning Hypertropia Downward




Exotropia Pediatric Ophthalmic Consultants
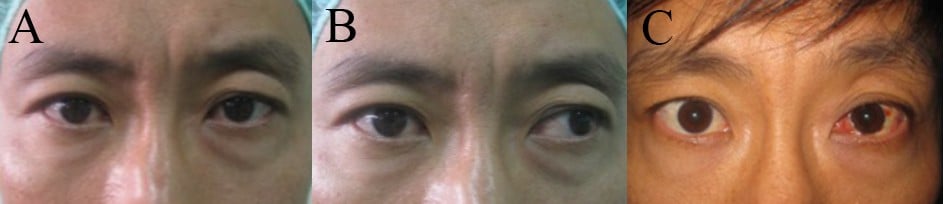
Exotropia is a form of strabismus (eye misalignment) in which one or both of the eyes turn outward It is the opposite of crossed eyes, or esotropia Exotropia may occur from time to time (intermittent exotropia) or may be constant, and is found in every age group See figures 1 and 2 Fig 1 Eyes alignedIm also being operated next week on the inner corner of both eyes, but for exotropia ) Wishing you a speedy recovery 2 Reply Share Report Save level 1 19d Wow how is that day 1?! Exophoria is similar to esophoria, as both conditions affect the coordination of the eyes However, while exophoria is an outward drift of the eyes, esophoria is an inward deviation Both conditions can be treated through the use of corrective lenses or vision therapy, though some cases don't require treatment




Exotropia Pediatric Ophthalmic Consultants




Exotropia In The Left Eye The Light Reflex Is Central In The Right Eye Download Scientific Diagram
Definition and Classification Infantile exotropia is a relatively rare strabismus disorder characterized by outward deviation of one or both eyes Onset is before age 6 months and persists beyond this age ( Figure 1 ) 1,2,3 It is classified as primary infantile exotropia, where patients are healthy with no evidence of systemic or ocular disease ( Table 1 ) 2 It usually occursTreatments include Glasses Glasses that help correct near or farsightedness will help keep the eyes aligned Patching People with exotropia tend to favor the aligned eye, so vision in the eye turned outward can weaken, resulting Exercises Your doctor may suggest aAn exotropia is an outward eye turn that can have a large variety of presentations It can be intermittent, constant, unilateral, alternating and vary in magnitude An exotropia has a variety of causes, some of which can be life threatening If an eyeturn is suspected or there is a family history of an eyeturn a comprehensive eyeexamination



Strabismus Ananthaksha Super Speciality Eye Hospital




Exotropia Ento Key
Exotropia is a common type of strabismus that occurs when misaligned eyes deviate outward Exotropia (also known as walleye or divergent strabismus) differs from its opposite form, esotropia (eye turns in toward nose), in that exotropic eyes point outward or away from the nose Exotropia can occur in one or both eyes Esotropia is a condition where one or both eyes turn inward The term derives from Greek, where 'eso' means 'inward,' and 'trope' means 'turn'Exotropia is an outward turning of one or both eyes It is a common type of strabismus About a quarter of all children with strabismus have exotropia There are different types of exotropia The condition can be visually noticeable either all the time or just sometimes



V Patterns Esotropia And Exotropia And Their Management By Dr Sudhir Singh
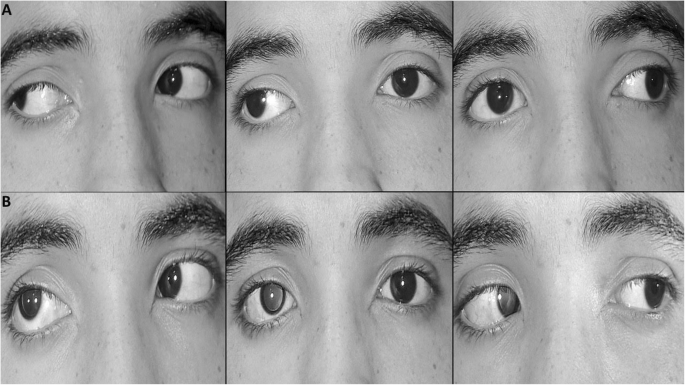



Management Of Stretched Scar Induced Secondary Strabismus Bmc Ophthalmology Full Text
Exotropia is a type of strabismus (misaligned eyes) in which one or both of the eyes turn outward The condition can begin as early as the first few months of life or any time during childhood Exotropia often begins as an intermittent problem, noticed only when the child is tired, sick, just waking up, excited, or stressedExotropia, a form of Strabismus, is the outward deviation (turn) of an eye and occurs in 12% of children by 7 years of age and occurs equally in males and females InExotropia one or both eyes turn outward away from the nose exotropia the edge of the lower eyelid turns in and causes the eyelashes to rub against the cornea entropion dry eye syndrome the eye is unable to produce enough tears to coat it xerophthalmia



Exotropia Left Eye Adult American Academy Of Ophthalmology



Seenso
Exotropia OPTOMETRIC CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE THE PRIMARY EYE CARE PROFESSION Doctors of optometry are independent primary health care providers who examine, diagnose, treat, and manage diseases and disorders of the visual one or both eyes, double vision, decreased vision, ocular discomfort, As a rule during the phoric phase of intermittent exotropia, the eyes are perfectly aligned and the patient will have bifoveal fusion with excellent stereoacuity ranging between 4060 second arc This excellent bifoveal fusion develops because the eyes are well aligned in early infancy when the critical binocular cortical connections are being Intermittent exotropia is the most common form of strabismus, characterized by an intermittent outward deviation of the eyes, affecting as much as 1% of the population 1,2 This condition most often presents in childhood and affects females more than males Control of the intermittent deviation can vary throughout the day 3,4




Exotropia




Diseases Of The Eye Strabismus A Variation Of Strabismus Exotropia Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image
It is an outward deviation of the eyes that may occur while fixating distance or near objects or both Exotropia can occur at any age but it is more common in early childhood between 14 years of ageEsophoria, like exophoria, is a condition that causes one eye to turn when covered The difference between the two conditions involves the direction in which the eye drifts or turns Esophoria causes an inward eye turn, as the eye drifts toward the nose Both eyes were then occluded, and the ocular deviation was remeasured Results The majority of patients (11/18) had a smaller deviation when both eyes were covered Occlusion of one eye resulted in a mean exotropia of 135° ± 47° Occlusion of both eyes reduced the mean exotropia to 60° ± 65° (paired ttest, P < 0001), corresponding




Intermittent Distance Exotropia Hull University Teaching Hospitals Nhs Trust




Everything You Need To Know About Cover Testing Eyedolatry
Constant exotropia This occurs when the eye turn is present all of the time, at all distances The serviceconnected postoperative congenital alternating strabismus (also called exotropia) is currently rated as 30 percent disabling under 38 CFR § 484, Diagnostic Code 6090 for diplopia It has been described both as monocular diplopia in the left eye, and as intermittent diplopia with both eyesCover testing with refractive correction in place revealed a 25∆ intermittent alternating exotropia (AX(T)) at distance with right eye fixation preference 90% of the time, and a 30∆ intermittent alternating exotropia (AX(T)') at near with right eye fixation preference 90% of the time




Exotropia Stock Photo Alamy




Exotropia American Association For Pediatric Ophthalmology And Strabismus
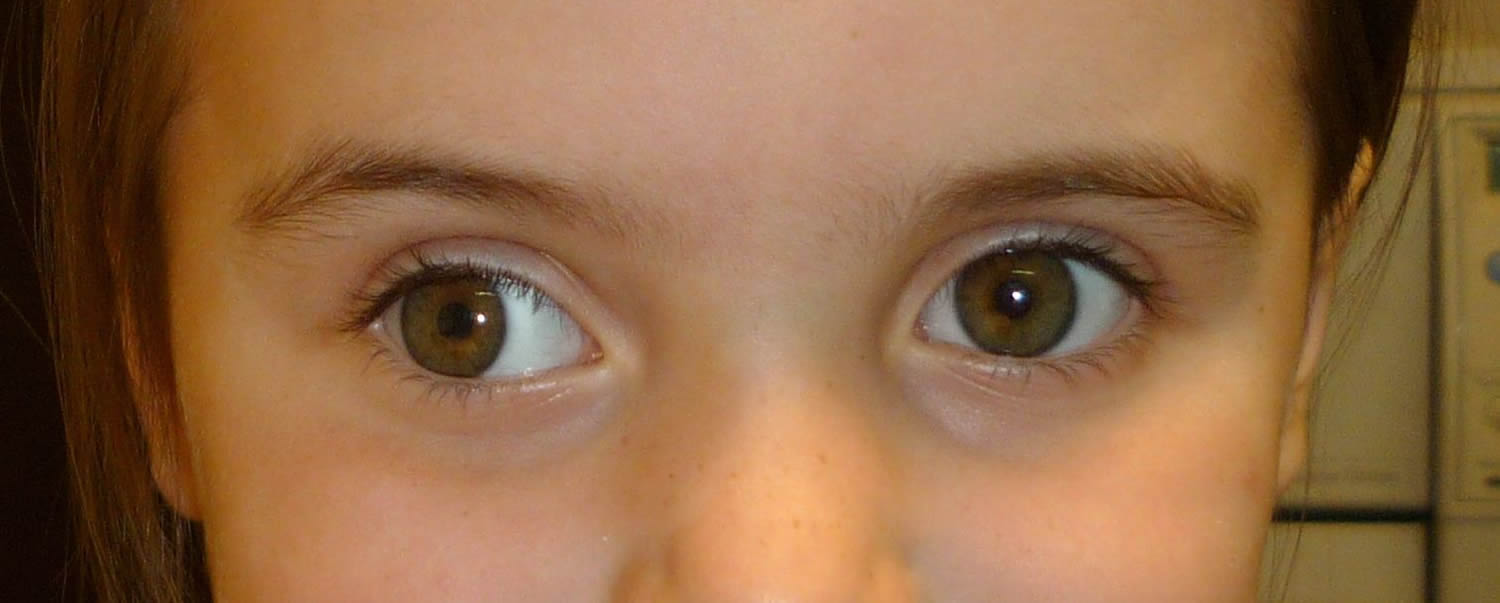
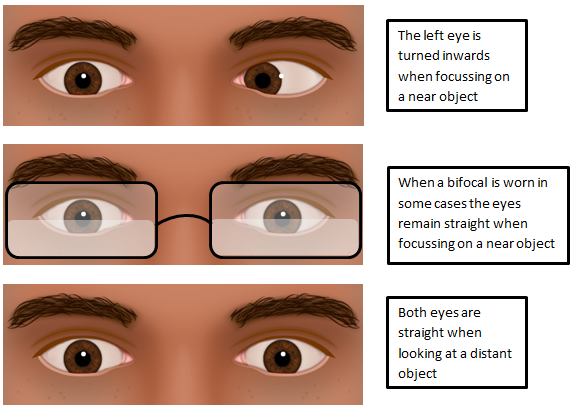
So exoTROPIA is a visible outward deviation of one or both eyes and exoPHORIA is only visible when testing eye position and breaking fusion The lines can get a bit blurred here – a phoria can break down into a tropia This means that a patient is able to keep both eyes teamed together, but at times one eye deviatesExotropia is a type of eye misalignment (known as strabismus) that occurs when one or both of the eyes turn outward This can be constant or only happen sometimes Exotropia is a category of Strabismus, a defect in which one's eyes deviate outward or away from each other The disease can either be in one eye or both Although Exotropia can occur at any age, younger children are majorly targeted The risks of Exotropia are equal in both male and female



Exotropia High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



1
Intermittent exotropia is a very common type of eye misalignment One or both eyes turn out toward the ear occasionally Only one eye turns out at a time while the other eye points straight forward Cause of intermittent exotropia The cause of this condition is not known Most experts believe that the brain of affected patients has trouble controlling theKellogg Eye Center Exotropia 1!! Childhood exotropia (outward deviation) is a horizontal exodeviation characterised by visual axis forming a divergent angle It usually begins as exophoria Exophoria is a condition in which eyes are straight without deviation when both eyes are open However, eye under cover deviates on coveruncover test or alternate cover test



Types Of Strabismus Esotropia And Exotropia Stock Photo By C Nnfotograf




Vision Therapy Success Story Strabismus Exotropia Eye Turn Outward Vision Therapy Philippines




Acquired Cyclic Exotropia And Hypotropia Sciencedirect




Variability Of Ocular Alignment In Primary Gaze A Patient 1 With Download Scientific Diagram



Exotropia Best Squint Treatment In Mumbai Eye Solutions




A Pre Surgical Examination Left Eye Le Hypertropia And Exotropia In Download Scientific Diagram



Strabismus Optometrist Optical Shop




Exotropia Symptoms Management And More



Strabismus Ananthaksha Super Speciality Eye Hospital



Outcomes Of Undercorrection In Surgical Management And Binocular Visio Opth




Exotropia In Cromwell Ct 4d Vision Gym




Exotropia Psychology Wiki Fandom




Exotropia In Children And Adults



Strabismus Amblyopia Neuro Vision Development Center



Strabismus Wikipedia



1




Consecutive Exotropia A Case Report And Review Of Literature



9 Gaze Photographs At Presentation Showing Large Angle Exotropia Download Scientific Diagram



O Xrhsths Amblyoplay Sto Twitter Intermittent Esotropia Is A Type Of Squint When An Individual Is Looking Beyond 3m No Squint Can Be Seen The Squint Is Only Seen When Focusing On




Exotropia Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




A Vision Disorder May Have Made Leonardo Da Vinci A Great Artist Rankred




What Is Exotropia Causes Symptoms Treatment Prognosis Complications



Exotropia Eye Specialist And Treatments In Gurgaon




Bilateral Superior Oblique Tenectomy For Exotropia With Vertical And Lateral Incomitance




Crossed Eyes Strabismus Squint Misaligned Eyes Dr Ali A Taqi Ppt Video Online Download




Strabismus 3d Illustration Showing Exotropia A Type Of Eye Deviation When Eye Turns Outward Stock Photo Picture And Royalty Free Image Image




What Is Exotropia Vision Express



Exodeviation




Four Types Of Strabismus Esotropia Exotropia Hydrotropia And Hypertropia Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image




Strabismus



Esophoria



Exotropia




Concerns In The Management Of Large Angle Horizontal Strabismus



Strabismus Dr Vryghem
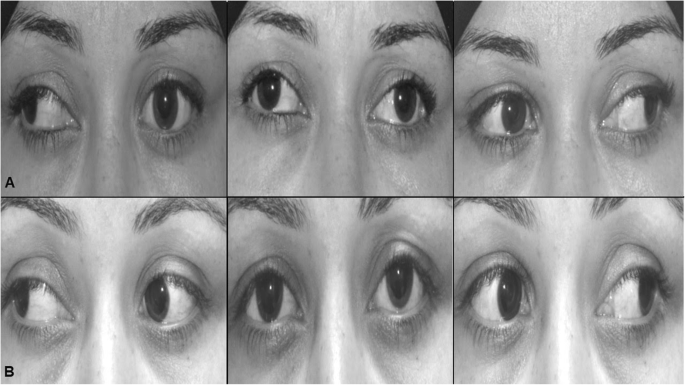



Management Of Stretched Scar Induced Secondary Strabismus Bmc Ophthalmology Full Text



Strabismus Kadrmas Eye Care New England
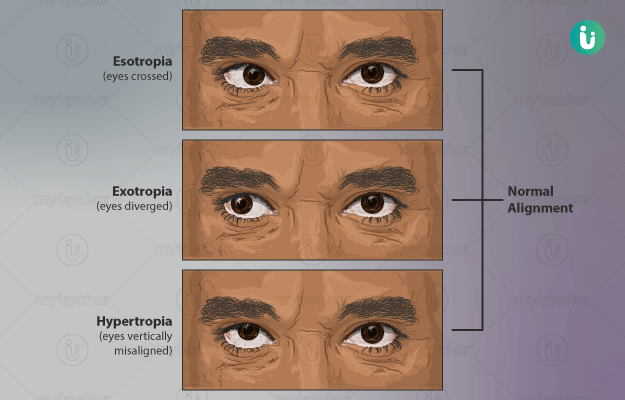



Cross Eyes Symptoms Causes Treatment Medicine Prevention Diagnosis




Providers In Charlotte Who Treat Strabismus



V Pattern Exotropia American Academy Of Ophthalmology




Intermittent Exotropia Ento Key
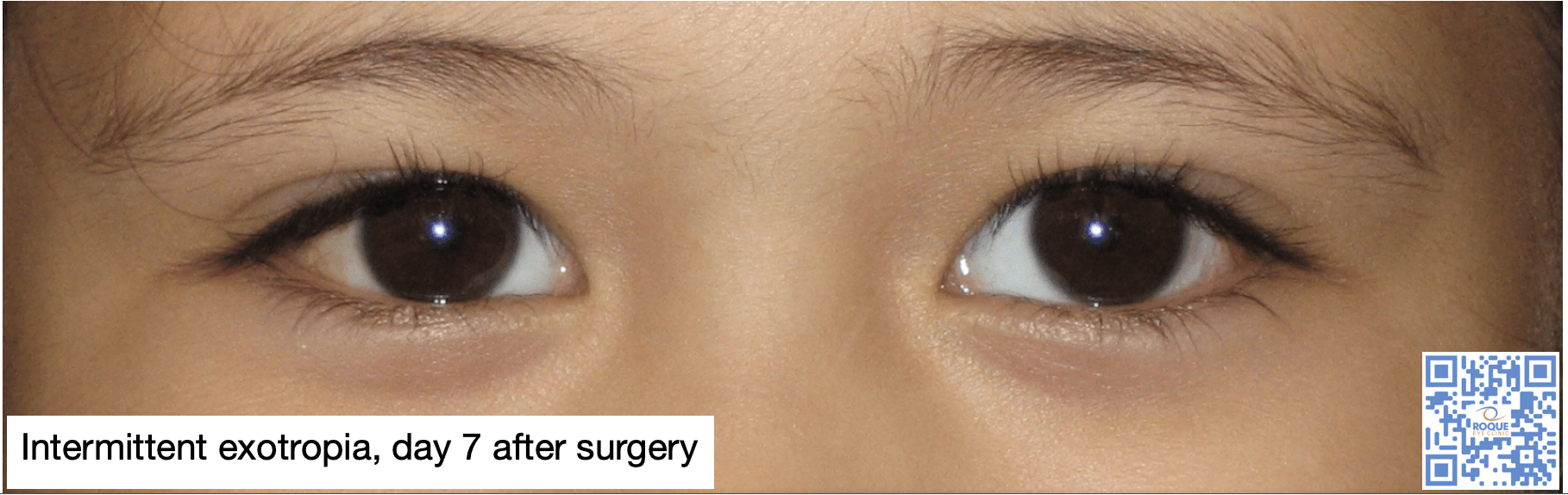



Intermittent Exotropia Roque Eye Clinic Eye Com Ph




Divergent Strabismus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Hypertropia Explore Facebook




What Is Exotropia Best Eye Care Hospital In Nagpur Madhav Netralaya




Consecutive Exotropia A Case Report And Review Of Literature




Strabismus



Ophthalmology Exotropia Dr Maria Elisa Scarale
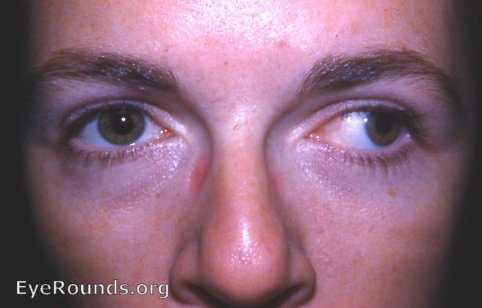



Exotropia Left Eye Eyerounds Org Online Ophthalmic Atlas




Outcomes Of Undercorrection In Surgical Management And Binocular Visio Opth




Strabismus Or Cross Eyed Vision Condition Vector Illustrations Stock Vector Illustration Of Medical Astigmatism
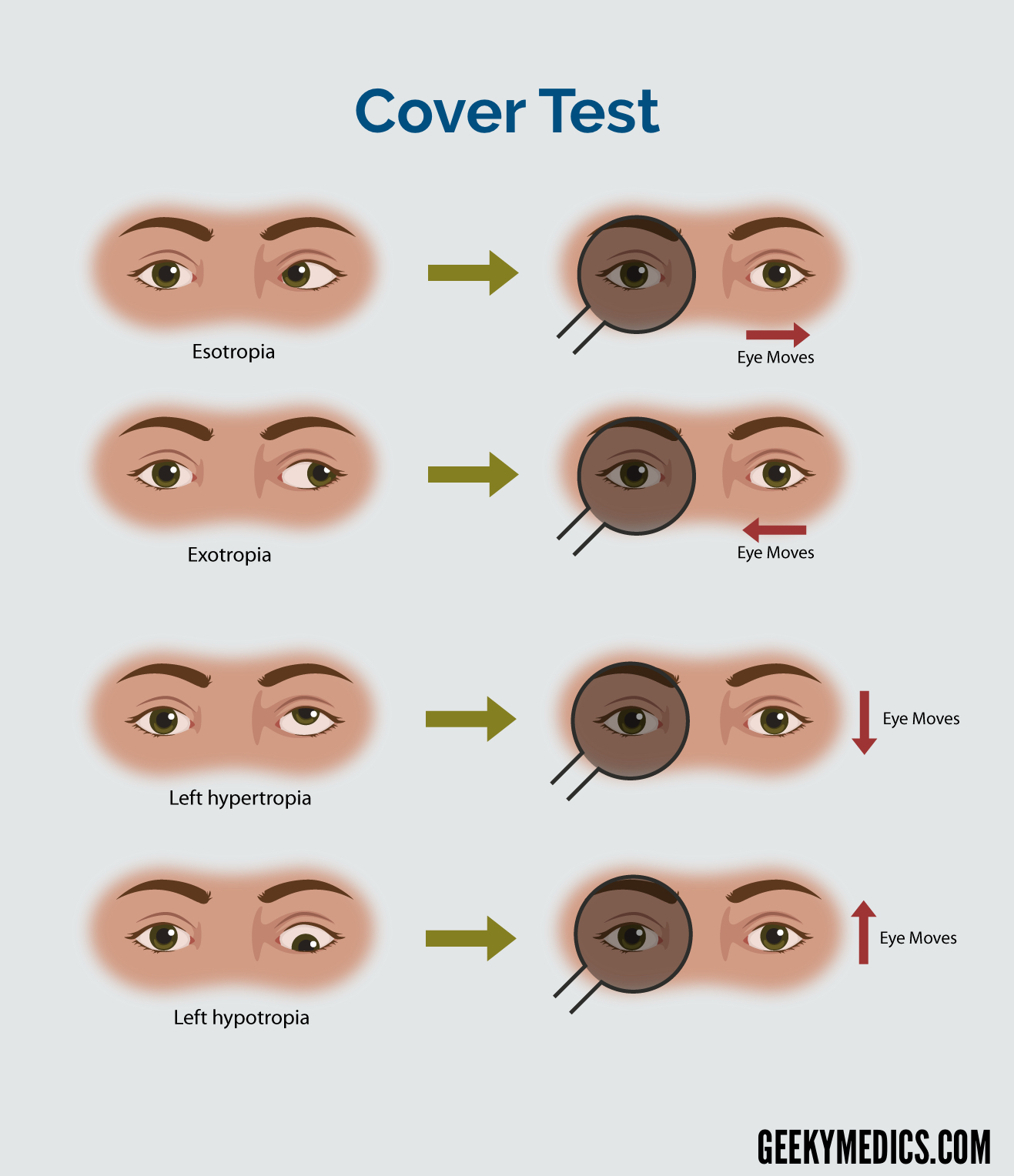



Strabismus Exotropia Esotropia Cover Test Geeky Medics




Eye Deviation Stock Illustrations 60 Eye Deviation Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Exophoria Definition Treatment And How It Compares To Exotropia
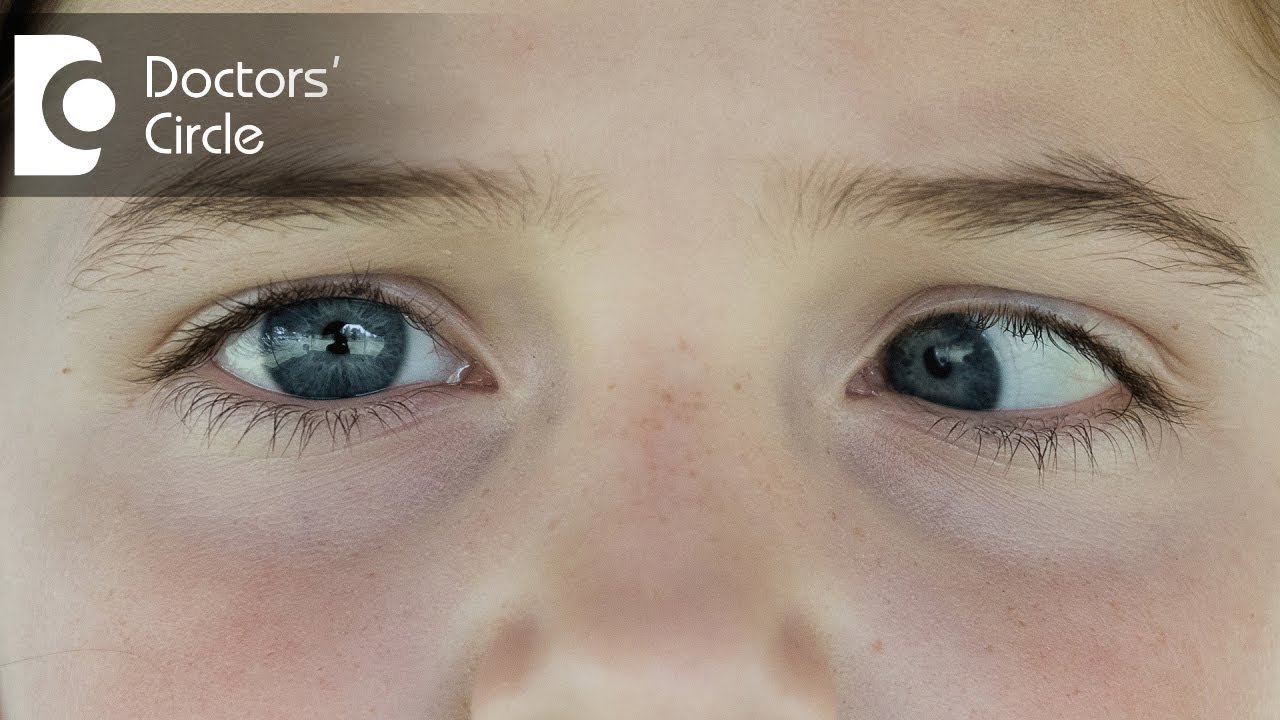




Can Exotropia Be Cured With Eye Drops Or Medicines Dr Sirish Nelivigi Youtube




Control Of Intermittent Exotropia Should Be Assessed With Control Of Intermittent Exotropia Should Be Assessed With




View Image




Case 1 Ptosis Hypotropia And Exotropia In The Patient S Left Eye Download Scientific Diagram




Strabismus American Association For Pediatric Ophthalmology And Strabismus




Strabismus Squint Strabismus Or Crossed Eyes Is The Inability To Point Both Eyes In The Same Direction At The Same Time One Eye May Appear To Turn In Esotropia Out Exotropia




Exotropia Types Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prevention



Exotropia Outward Deviation Of The Eye
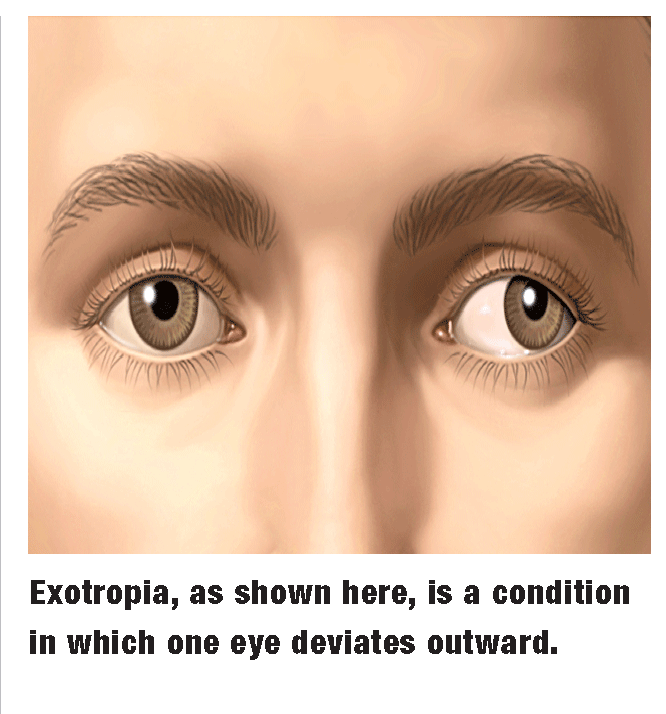



Do You See A Pattern
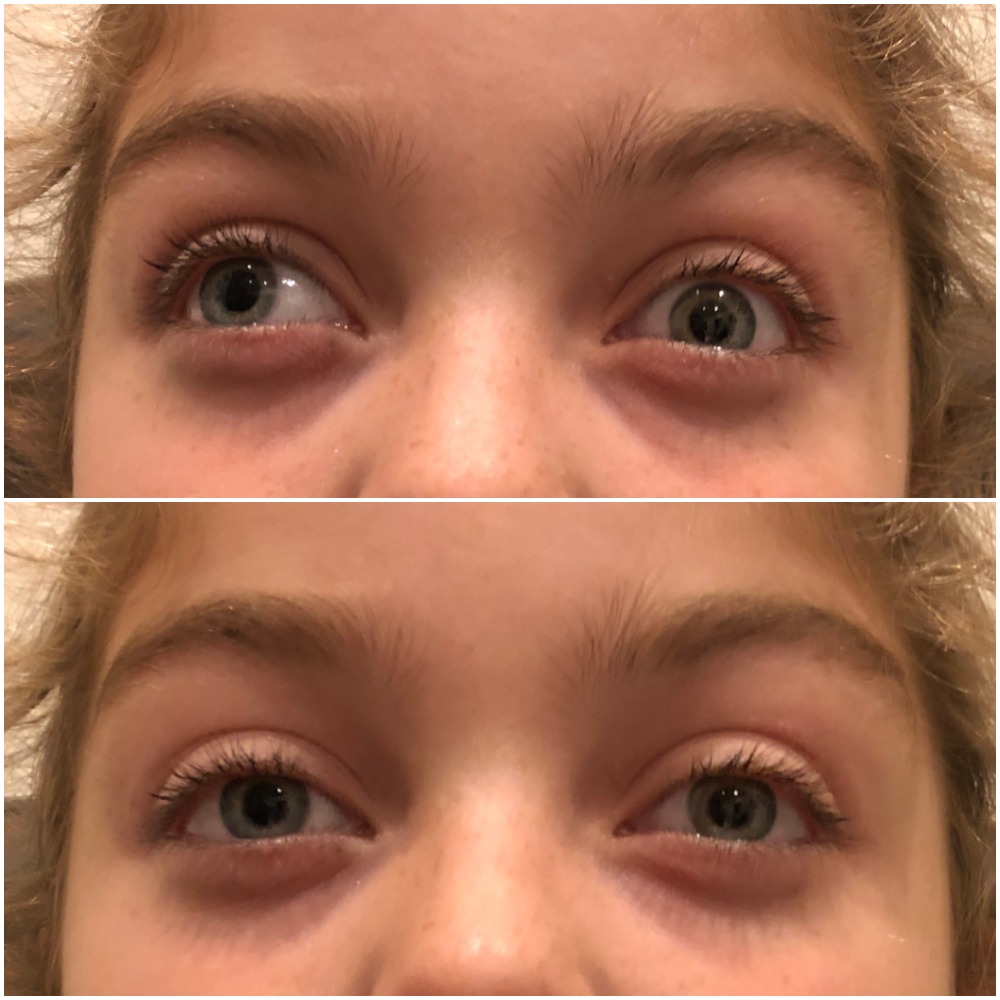



Non Surgical Correction Of Exotropia Dr Claudia Lee Optometrist




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Vector Illustration Of Normal Human Eyes And Eyes With Problem Strabismus Or Crossed Eyes Types Esotropia Exotropia Hypertropia Hypotropia For Advertisement And Medical Publications Eps 10 موقع تصميمي




Exotropia Hypotropia Complex In High Myopia Semantic Scholar



What Is Exotropia Vision Express




Exotropia Pediatric Ophthalmic Consultants




Pediatric Ophthalmology Flashcards Quizlet




Wall Eyed Bilateral Internuclear Ophthalmoplaegia Webino From A Paramedian Mesencephalic Infarct Bmj Case Reports




Strabismus




What Is Exotropia Bard Optical



Strabismus Portland Pediatric Eye Care Portland Oregon




Cause Of V Pattern Strabismus In Craniosynostosis A Case Report British Journal Of Ophthalmology



The Different Types Of Vision Problems




Stock Image Divergent Strabismus A Deviation Of The Eyes Strabismus In Which One Or Both Eyes Are Directed Outward It Is Also Called Exotropia Or Walleye 01b0v9cz Ism Search




Pdf Supermaximal Recession And Resection In Large Angle Sensory Exotropia Semantic Scholar




Squint Treatment Exotropia Neo Eye Clinic



1




Exotropia



Exotropia Liberal Dictionary




Exotropia Ento Key




Exotropia Dr Lionel Kowal Franzco Fracs Melbourne Australia Ppt Download




Strabismus



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿